Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental condition that affects the gums and tissues surrounding the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth and gums, which can lead to inflammation and infection. Gum disease can range from mild gingivitis, which causes redness and bleeding of the gums, to more severe periodontitis, which can result in tooth loss and damage to the supporting bone structure. Gum disease treatment typically involves a combination of professional cleaning, medication, and improved oral hygiene habits. Early detection and treatment of gum disease is important to prevent further damage and preserve overall oral health.

What is Gum Disease Treatment?
Gum disease treatment typically involves several steps to control the infection, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage to the gums and teeth. The first step is usually a professional dental cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and below the gum line. Antibacterial medications may also be prescribed to control the infection. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or regenerate damaged tissue, or to remove severely infected teeth. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, and scheduling regular dental check-ups can also help prevent and manage gum disease. Your dentist or periodontist will determine the best course of treatment based on the severity of your gum disease and individual needs.
How Does Gum Disease Develop?
Gum disease develops when bacteria and plaque accumulate on and around the teeth and gums. When these substances are not removed through regular brushing and flossing, they can cause irritation and inflammation of the gums, leading to the early stages of gum disease, known as gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis, which can result in irreversible damage to the teeth and gums. Other factors that can contribute to the development of gum disease include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and genetics. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene habits are essential in preventing and managing gum disease.
How Is Gum Disease Linked to Other Health Issues?
Gum Disease and Heart Attacks
Research has shown that gum disease is linked to other health problems such as heart attacks. When left untreated, the bacteria and inflammation associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, potentially contributing to a variety of health issues. For example, gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, respiratory infections, and pregnancy complications. While the exact mechanisms behind these connections are not yet fully understood, maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking treatment for gum disease can help reduce the risk of developing these and other health problems.
More Questions about Gum Disease?
Contact our office today to schedule a consultation with our dentist. We can answer any questions you have about gum disease treatment and address any issues unique to your specific situation.
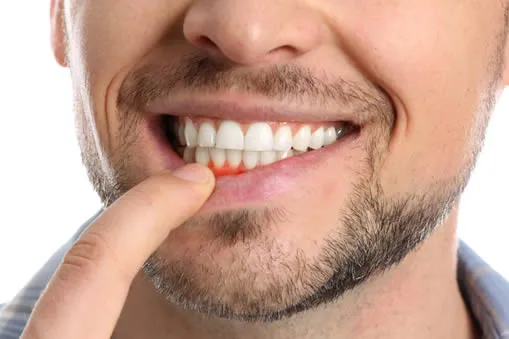
What Are the Symptoms or Signs of Gum Disease?
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums or teeth that appear longer
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite or chew
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Changes in the alignment of teeth or a change in the way partial dentures fit
It is important to note that some people with gum disease may not experience any symptoms, which is why regular dental check-ups with our Sunrise dentist are essential in detecting and managing the condition.
How Your Dentist Identifies Periodontal Disease
Visual exam
The dentist or dental hygienist will visually inspect your teeth and gums, looking for signs of redness, swelling, bleeding, or other signs of inflammation.
Pocket depth measurement
The dentist or dental hygienist will use a probe to measure the depth of the pockets between your teeth and gums. Deeper pockets may indicate the presence of gum disease.
X-rays
X-rays can help detect bone loss or other structural changes that may indicate gum disease.
Medical history
Your dental professional will ask about your medical history, including any medications or health conditions that may contribute to gum disease.
Contact our office today to schedule a consultation. We can answer any questions you have and address any issues unique to your situation.
How Is Periodontal Disease Treated?
First, a thorough cleaning of the teeth and gums is performed to remove plaque and tartar build-up. Antibacterial medication may also be prescribed to control the infection. In more advanced cases, the dentist may perform scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or regenerate damaged tissue, or to remove severely infected teeth. With proper treatment and ongoing oral care, gum disease can be managed, and the health of the gums and teeth can be restored. Contact us at The Dental Office of Dianna Wohlstein, DMD today.